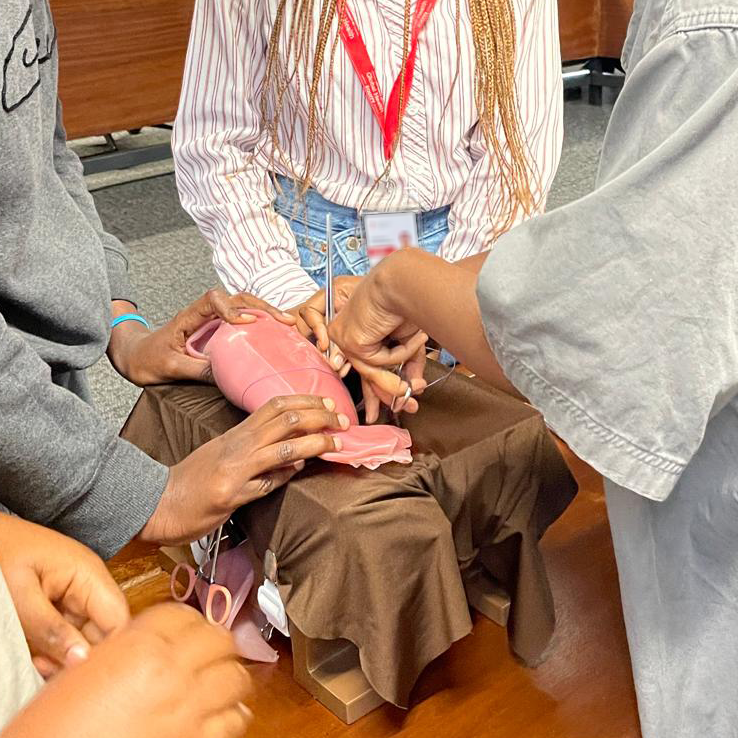
What is Postpartum Hemorrhage?
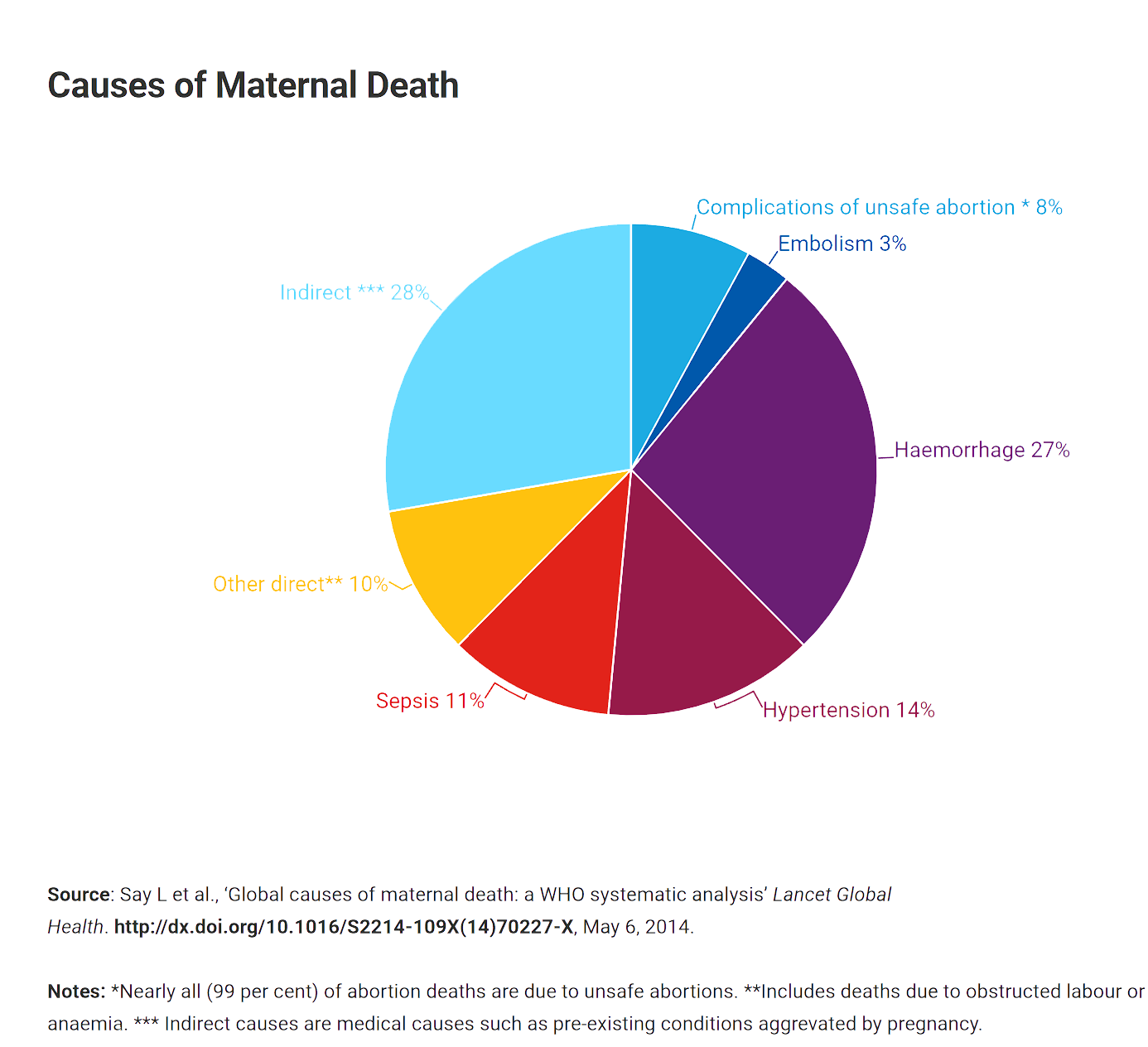
Although childbirth is often a joyous occasion, it is also one that may be fraught with unanticipated suffering and loss. The leading cause of maternal deaths worldwide is postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) or excessive bleeding after childbirth. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 14 million women experience PPH each year, resulting in 70,000 maternal deaths around the world annually.1 This amounts to 200 deaths per day or a maternal death every eight minutes.2
Global Disparities in Maternal Mortality
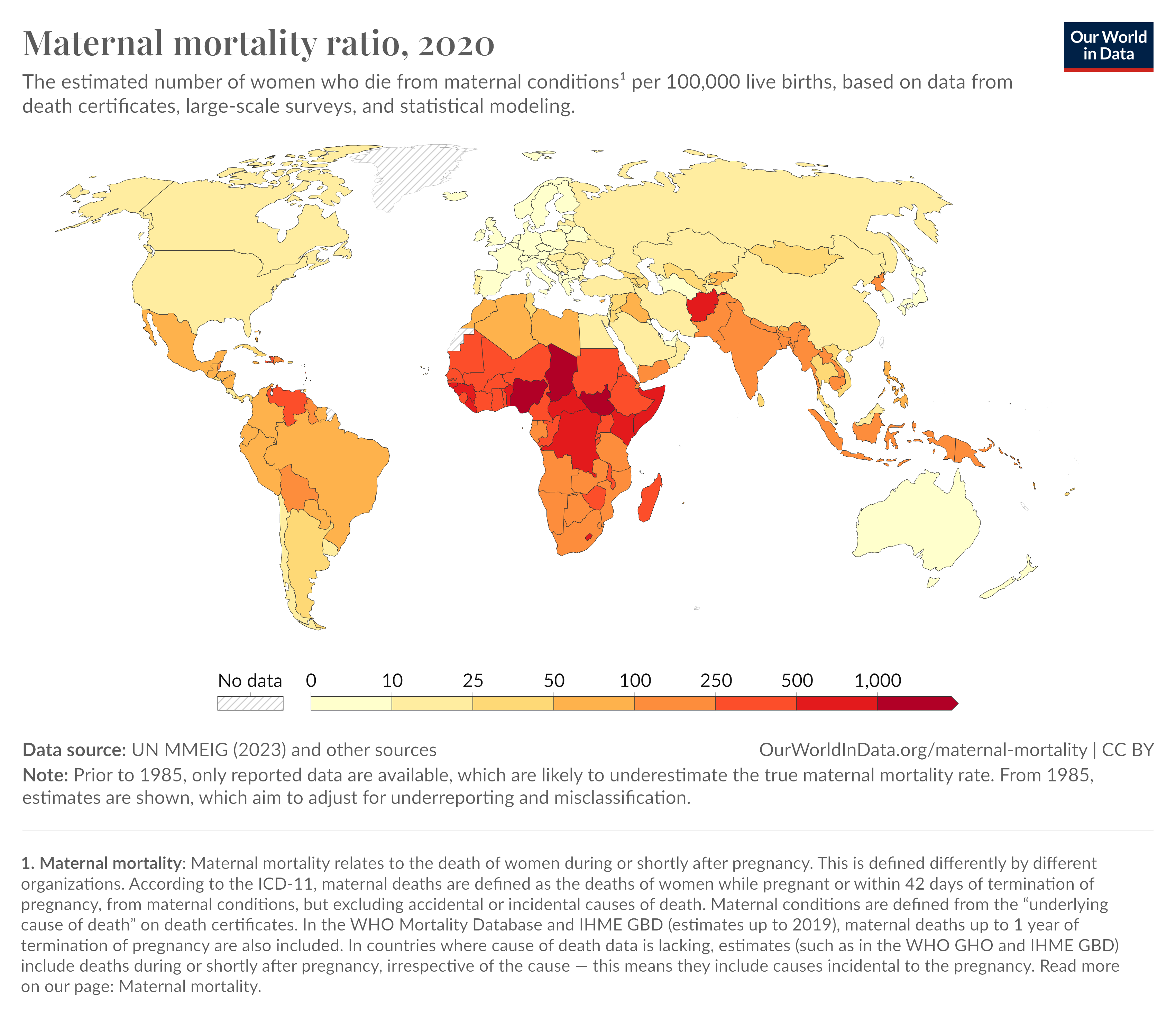
These maternal deaths are inequitably distributed globally and the burden is largely borne by women who live in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where, on average, 545 maternal deaths occur in every 100,000 births.2 By comparison, 11 maternal deaths occur in every 100,000 live births in Canada. In other words, the maternal mortality ratio (MMR), defined as the number of maternal deaths per 100,000 live births, is 50 times higher in LMICs than in Canada.3 Despite these staggering numbers, with adequate and timely interventions – including advanced surgical techniques – the majority of these devastating deaths are preventable and progress may be made towards achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3’s (SDG3) Target 3.1 “decrease the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70”.4 Furthermore, such interventions will provide a viable pathway to achieve WHO’s aim to have by 2030, “no country with a maternal mortality ratio greater than 140”.5
Our Solution. STITCH.
STITCH fills a gap in current surgical education as an innovative, portable, reusable intermediate fidelity simulator that is accessible to end-users all over the world. It addresses a critical skillset which cuts across healthcare provider cadres in both rural and urban settings. STITCH harnesses the evidence-based power of simulation and the synergies of Biomedical Engineering and Obstetrics/Gynecology expertise to scale up surgical capacity in life-saving procedures to treat PPH.
The base, skin, and ureters are reusable. The uterus can withstand up to 20 rounds of compression sutures and uterine artery ligation. After sub-total hysterectomy, the uterus/pelvic organ entity will need to be replaced.
